- Giới thiệu migration
- Tạo dự án mới thực hành migration
- Tạo Migration thứ nhất
- Thực hiện Migrate
- Tạo Migration thứ hai
- Tạo Migration thứ ba
- Tạo Migration với DB có trước
- Tùy biến Migration
- Tóm tắt lệnh Migration
Giới thiệu migration
Migration là kỹ thuật trong việc tương tác với cơ sở dữ liệu, theo đó việc thay đổi về cấu trúc CSDL ở code sẽ được cập nhật lên CSDL đảm bảo dữ liệu đang tồn tại không bị mất, lịch sử (phiên bản) cập nhật được lưu lại sau mỗi lần cập nhật.
Thường khi sử dụng EF làm việc với DB, có hai cách đó là
làm việc với một CSDL đang tồn tại (gọi là database first) - việc cập nhật database thực hiện khá
độc lập với ứng dụng - tình huống này Migration ít hữu ích, tuy nhiên trường hợp bạn tạo database từ code, thay
đổi cấu trúc database ... bằng code thì migration rất hữu ích. Tất nhiên ta vẫn có cách để sử dụng EF Migration
trên database đã tồn tại.
Với migration khi bạn cập nhật Model, yêu cầu database cập nhật thì nó sẽ lưu thông tin phiên bản hiện tại của
cấu trúc Model (database) ở Server DB - ví dụ phiên bản a, sau đó thay đổi các Model, lại yêu cầu
cập nhật thì nó sẽ đọc thông tin phiên bản cuối trên DB, so sánh sự khác biệt và cập nhật sự khác biệt đó để lên phiên
bản mới, phiên bản b.
Tạo dự án để thực hành EF Migration
Tạo một dự án kiểu console, trong thư mục EFMigration, có cài đặt các package để làm việc được với
EF
dotnet add package System.Data.SqlClient dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools.DotNet # .NET 3.0 trở đi cài lệnh dotnet ef bằng dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef
Tạo ra hai Model đơn giản sau:
Models/Article.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFMigration.Models
{
[Table("article")]
public class Article
{
[Key]
public int ArticleId {set; get;}
[StringLength(100)]
public string Title {set; get;}
}
}
Models/Tag.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFMigration.Models
{
public class Tag
{
[Key]
[StringLength(20)]
public string TagId {set; get;}
[Column(TypeName="ntext")]
public string Content {set; get;}
}
}
Triển khai một DbContext (WebContext) sử dụng 2 Model trên
Models/WebContext.cs
using System;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Infrastructure;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace EFMigration.Models
{
public class WebContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Article> articles {set; get;} // bảng article
public DbSet<Tag> tags {set; get;} // bảng tag
// chuỗi kết nối với tên db sẽ làm việc đặt là webdb
public const string ConnectStrring = @"Data Source=localhost,1433;Initial Catalog=webdb;User ID=SA;Password=Password123";
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(ConnectStrring);
optionsBuilder.UseLoggerFactory(GetLoggerFactory()); // bật logger
}
private ILoggerFactory GetLoggerFactory()
{
IServiceCollection serviceCollection = new ServiceCollection();
serviceCollection.AddLogging(builder =>
builder.AddConsole()
.AddFilter(DbLoggerCategory.Database.Command.Name,
LogLevel.Information));
return serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider()
.GetService<ILoggerFactory>();
}
}
}
Do sử dụng kỹ thuật migration để tạo và thay đổi
database nên đừng sử dựng EnsureCreatedAsync như các
ví dụ trước (nếu làm vậy cần xử lý như là database first - xem phần sau).
Tạo Migration
Lệnh tạo ra một Migration, giả sử đặt tên cho nó là NameMigration sử dụng lệnh sau:
dotnet ef migrations add NameMigration
Thay NameMigration bằng tên do bạn đặt, nó mang ý nghĩa như là phiên bản, nó cũng được dùng để đặt
tên những lớp phát sinh.
Bản đầu tiên áp dụng cho ví dụ sẽ đặt tên là InitWebDB
dotnet ef migrations add InitWebDB
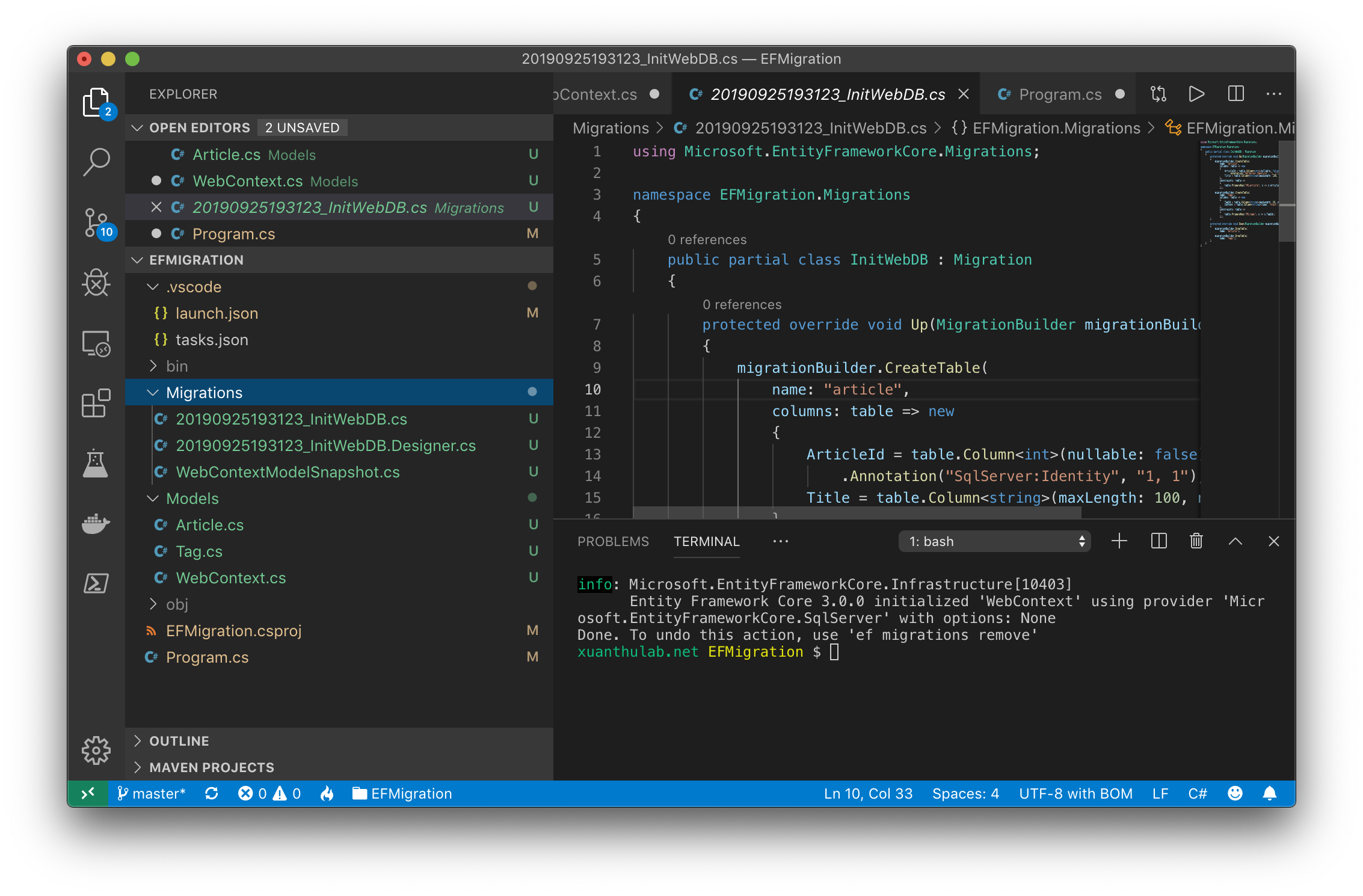
Sau lệnh này, nó tạo ra 3 file trong thư mục Migrations các file có tên dạng:
20190925193123_InitWebDB.cs 20190925193123_InitWebDB.Designer.cs WebContextModelSnapshot.cs
Số 20190925193123 sinh ra theo thời điểm chạy lệnh. 3 file này chứa thông tin để có thể cập nhật (hoặc tạo)
database đúng cấu trúc Model ở thời điểm mà bạ tạo Migration.
WebContextModelSnapshot.cs là snapshot (ảnh chụp) để tạo được cấu trúc database theo các Model hiện tại.
Mở xem thử nội dung xem:
// <auto-generated />
using EFMigration.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Infrastructure;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Storage.ValueConversion;
namespace EFMigration.Migrations
{
[DbContext(typeof(WebContext))]
[Migration("20190925193123_InitWebDB")]
partial class InitWebDB
{
protected override void BuildTargetModel(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
#pragma warning disable 612, 618
modelBuilder
.HasAnnotation("ProductVersion", "3.0.0")
.HasAnnotation("Relational:MaxIdentifierLength", 128)
.HasAnnotation("SqlServer:ValueGenerationStrategy", SqlServerValueGenerationStrategy.IdentityColumn);
modelBuilder.Entity("EFMigration.Models.Article", b =>
{
b.Property<int>("ArticleId")
.ValueGeneratedOnAdd()
.HasColumnType("int")
.HasAnnotation("SqlServer:ValueGenerationStrategy", SqlServerValueGenerationStrategy.IdentityColumn);
b.Property<string>("Title")
.HasColumnType("nvarchar(100)")
.HasMaxLength(100);
b.HasKey("ArticleId");
b.ToTable("article");
});
modelBuilder.Entity("EFMigration.Models.Tag", b =>
{
b.Property<string>("TagId")
.HasColumnType("nvarchar(20)")
.HasMaxLength(20);
b.Property<string>("Content")
.HasColumnType("ntext");
b.HasKey("TagId");
b.ToTable("tags");
});
#pragma warning restore 612, 618
}
}
}
Mỗi một Migration có một lớp kế thừa từ lớp Migration được tạo ra, trong nó có hai phương thức là
Up và Down - để thực hiện chuyển từ phiên bản thấp đến phiên bản này (Up) hoặc đang từ
phiên bản này lùi về phiên bản trước (Down). Lớp này được định nghĩa trong 2 file mã nguồn còn lại, ví dụ
trong file: 20190925193123_InitWebDB.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations;
namespace EFMigration.Migrations
{
public partial class InitWebDB : Migration
{
protected override void Up(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "article",
columns: table => new
{
ArticleId = table.Column<int>(nullable: false)
.Annotation("SqlServer:Identity", "1, 1"),
Title = table.Column<string>(maxLength: 100, nullable: true)
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_article", x => x.ArticleId);
});
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "tags",
columns: table => new
{
TagId = table.Column<string>(maxLength: 20, nullable: false),
Content = table.Column<string>(type: "ntext", nullable: true)
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_tags", x => x.TagId);
});
}
protected override void Down(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.DropTable(
name: "article");
migrationBuilder.DropTable(
name: "tags");
}
}
}
Thực hiện Migration
Bạn có thể thực hiện migrate (tạo nếu chưa có, cập nhật nếu cần) từ code, như:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using EFMigration.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFMigration
{
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
using (var webcontext = new WebContext())
{
// Thực hiện Migrate - tạo db đúng cấu trúc Migration cuối cùng nếu chưa có
// Nếu DB đã có từ các Migration trước, sẽ cập nhật
await webcontext.Database.MigrateAsync();
}
}
}
}
Tuy nhiên thường thực hiện Migrate bằng gõ lệnh sau (nên làm cách này) để cập nhật DB như migration cuối cùng:
dotnet ef database update
Trong trường hợp muốn chuyển DB về cấu trúc ở bản Migration nào đó (khi đang có nhiều Migration) thì chỉ rõ tên
migration trong lệnh. Ví dụ - tên phiên bản đầu tiên InitWebDB thì gõ:
dotnet ef database update InitWebDB
Bạn chú ý là nếu muốn xóa DB (cẩn thận) để thực hiện lại thì có thể gõ lệnh:
dotnet ef database drop -f
Sau khi thực hiện Migration, do chưa có DB nó đã tạo ra DB đúng theo cấu trúc Model
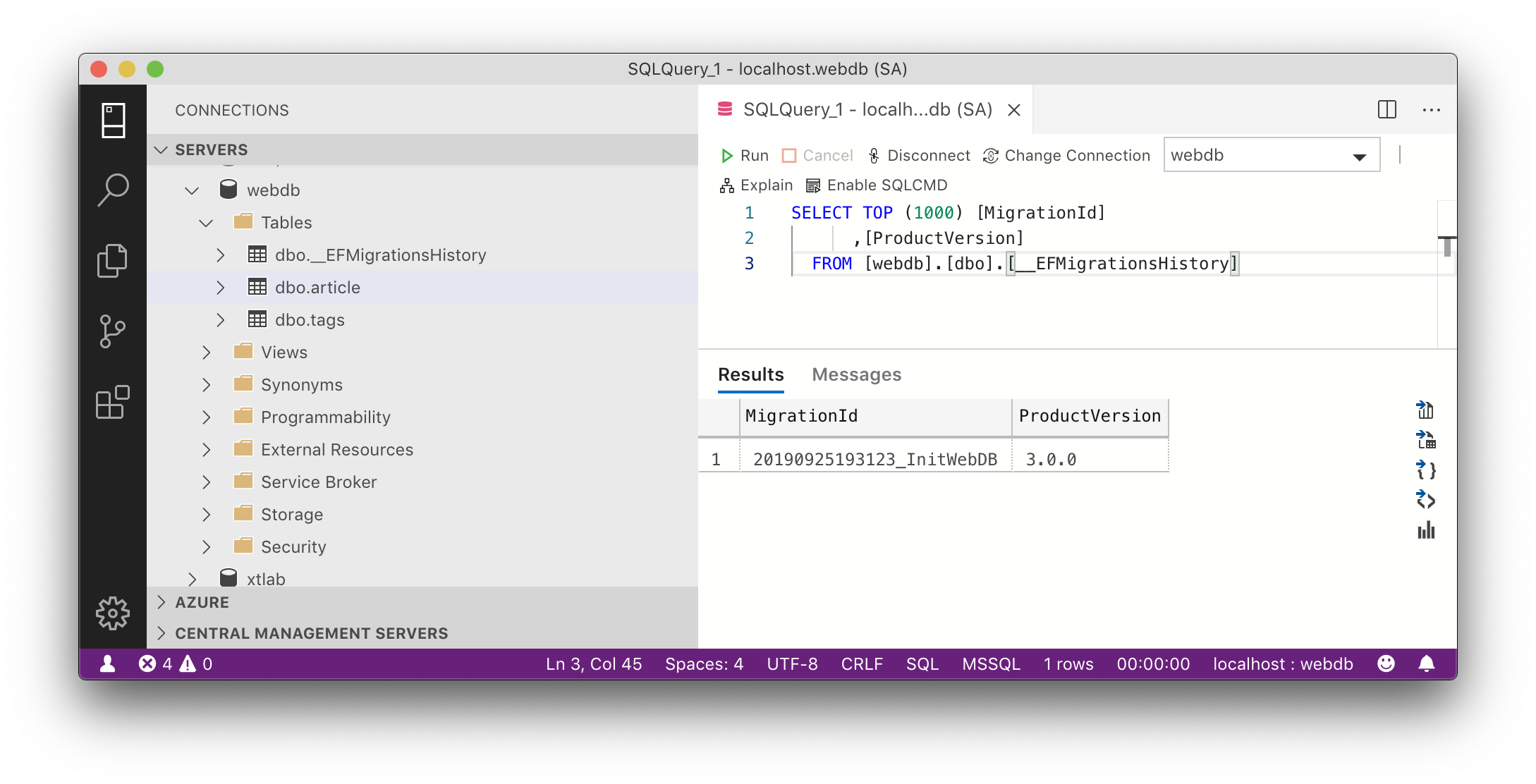
Ngoài các bảng theo Model, có thêm bảng __EFMigrationsHistory chứa thông tin lịch sử cập nhật
bởi Migration. Từ bảng này, EF Migration biết được DB đang ở phiên bản nào
Tạo Migration thứ 2
Để tìm hiểu kỹ hơn, tiến hành sửa đổi cập nhật Model như sau: cho vào Model Article
một trường mới
/..
public class Article
{
/..
// Cột thêm vào khi cập nhật lần 2
[Column(TypeName="ntext")]
public string Content {set; get;}
}
}
Sau khi thực hiện thay đổi các Model như vậy, tiến hành tạo ra một Migration mới đặt tên là InitWebDB-V1
dotnet ef migrations add InitWebDB_V1
Nó đã tạo ra Migration tiếp theo Migrations/20190925204118_InitWebDB_V1.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations;
namespace EFMigration.Migrations
{
public partial class InitWebDB_V1 : Migration
{
protected override void Up(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.AddColumn<string>(
name: "Content",
table: "article",
type: "ntext",
nullable: true);
}
protected override void Down(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.DropColumn(
name: "Content",
table: "article");
}
}
}
Đồng thời Snapshot có thêm:
/..
b.Property<string>("Content")
.HasColumnType("ntext");
/..
Thực hiện Migrate
dotnet ef database update InitWebDB_V1
Kết quả như hình, với database có cấu trúc mới
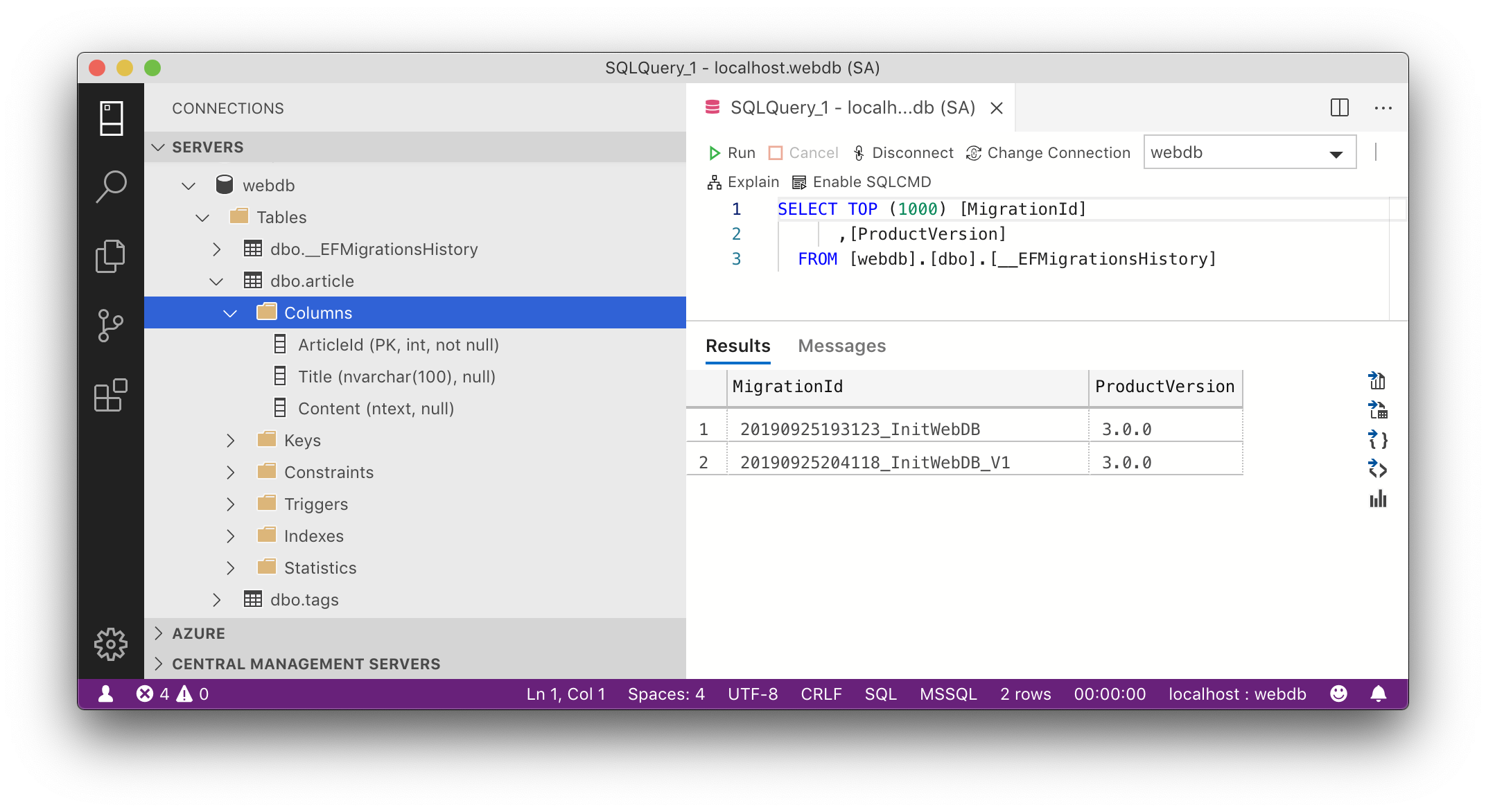
Tạo Migration thứ 3
Tạo mới model tên ArticleTag là bảng chứa thông tin về các Tag của bài viết Article
Tạo Model mới Models/ArticleTag.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFMigration.Models
{
[Table("articletag")]
public class ArticleTag
{
[Key]
public int ArticleTagId {set; get;}
public int ArticleId {set; get;}
[ForeignKey("ArticleId")]
public Article article {set; get;}
[StringLength(20)]
public string TagId {set; get;}
[ForeignKey("TagId")]
public Tag tag {set; get;}
}
}
Thêm thuộc tính vào WebContext
public DbSet<ArticleTag> articleTags {set; get;}
Cũng thêm WebContext phương thức OnModelCreating trong đó thiết lập Index cho bảng mới.
/..
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<ArticleTag>(entity => {
// Tạo Index Unique trên 2 cột
entity.HasIndex(p => new {p.ArticleId, p.TagId})
.IsUnique();
});
}
/..
Tương tự như trên tạo ra bản Migration tiếp theo:
dotnet ef migrations add InitWebDB_V2
Cập nhật vào DB
dotnet ef database update InitWebDB_V2
Xóa Migration cuối với lệnh
dotnet ef migrations remove
Liệt kê các Migration
dotnet ef migrations list
Nếu muốn tạo SQL Script cho Migration thì gõ
dotnet ef migrations script --output migrations.sql
Kết quả xuất ra migrations.sql
Bạn có thể quay về một phiên bản bất kỳ trong danh sách bằng cách thực hiện
lệnh dotnet ef database update tên_quay_về
Mã nguồn hoặc tải về ex046
Tạo Migration với Db đã có
Nếu dự án đã có DB trước rồi (có cả dữ liệu), giờ mới bắt đầu sử dụng Migration, thì trước tiên tạo ra các Model, DbContext từ DB có sẵn theo hướng dẫn - dbcontext scaffold
Tiếp theo cần tạo Migration đầu tiên như hướng dẫn trên, ví dụ migration đầu tiên đặt tên là Init
dotnet ef migrations add Init
Tuy nhiên nếu thực hiện update sẽ lỗi vì DB đã có và trong lịch sử không có lưu thông tin gì về Migration
Để thiết lập Migration này đã thực hiện và lưu trong lịch sử DB thì gõ lệnh tạo ra SQL Migration
dotnet ef migrations script --output migrations.sql
Mở migrations.sql lấy và thực hiện trực tiếp câu lệnh SQL liên quan đến bảng __EFMigrationsHistory
gồm các SQL tạo bảng __EFMigrationsHistory, Insert vào bảng __EFMigrationsHistory,
tạo bảng đó bằng cách chạy trực tiếp SQL
CREATE TABLE [__EFMigrationsHistory] (
[MigrationId] nvarchar(150) NOT NULL,
[ProductVersion] nvarchar(32) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK___EFMigrationsHistory] PRIMARY KEY ([MigrationId])
);
Sau đó lấy MigrationID bằng cách gõ lệnh:
dotnet ef migrations list
Nó hiện thị thông tin:
Build started... Build succeeded. 20200826095315_Init
Qua đó biết được MigrationID đầu tiên là: 20200826095315_Init
Thực hiện tiếp lấy Version của công cụ:
dotnet ef --version
Nó hiện thị thông tin:
Entity Framework Core .NET Command-line Tools 3.1.7
Vậy phiên bản là 3.1.7, thực lệnh câu lệnh SQL chèn một dòng vào bảng:
INSERT INTO [__EFMigrationsHistory](MigrationId, ProductVersion)
VALUES ('20200826095315_Init', '3.1.7')
Từ đây, các Migration tiếp theo (không phải Migration Init) sẽ thực hiện bình thường
Tùy biến Migration
Trong các phiên bản Migration, code của nó có hai phương thức là Up và Down,
tại đây bạn có thể thi hành các lệnh SQL, nếu thi hành trong Up thì là khi cập nhật, thi hành trong Down
là khi revert về phiên ban cũ.
Để thi hành các câu lệnh SQL bạn thực hiên
migrationBuilder.Sql("câu-lệnh-sql")
Tóm tắt các lệnh với Migration
| Lệnh | Ý nghĩa |
|---|---|
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef |
Cài đặt công cụ dotnet ef |
dotnet tool update --global dotnet-ef |
Cập nhật công cụ dotnet ef |
dotnet ef migrations add NameMigration |
Tạo một Migration có tên NameMigration |
dotnet ef migrations list |
Danh sách các Migration |
dotnet ef database update |
Cập nhật Database đến Migration cuối |
dotnet ef database update NameMigration |
Cập nhật Database đến Migration có tên NameMigration |
dotnet ef migrations remove |
Xóa migration cuối |
dotnet ef migrations script --output migrations.sql |
Xuất lệnh SQL khi thực hiện Migration |
dotnet ef database drop -f |
Xóa database |

